What is a Bone Marrow Transplant?
What is a Bone Marrow Transplant?
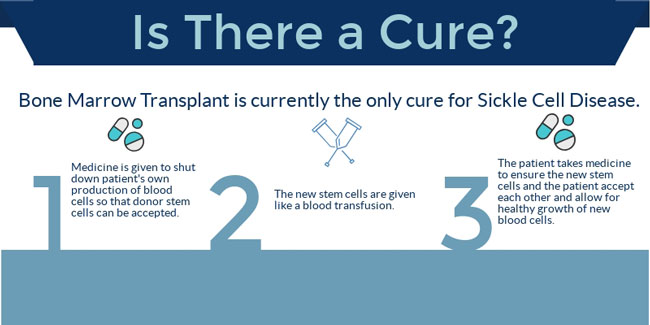
Blood and Marrow Transplantation (BMT) is the only readily available cure for Sickle Cell Disease. BMT is only broadly available for patients with a matched sibling donor. Unrelated and mis-matched related BMT is only available through clinical trials.
BMT replaces the patient’s bone marrow that produces abnormal red blood cells with marrow from a donor that produces normal red blood cells. Bone marrow cells are drawn from the pelvic bone of the donor. The bone marrow graft is administered through the veins.
BMT Limitations
BMT limitations include:
- Graft rejection
- Infertility caused by chemotherapy before BMT
- Graft vs Host Disease (GVHD)
What is Graft vs Host Disease?
GVHD occurs when the donor’s immune cells react against the patient’s body. It can cause severe injury to the patient’s gastrointestinal tract and other organs. It can be chronic or sometimes fatal. GVHD is uncommon in young children who receive a transplant from a matched sibling donor. It is more common in adolescents and those who receive a transplant from an unrelated donor.

